Lacunae Histology
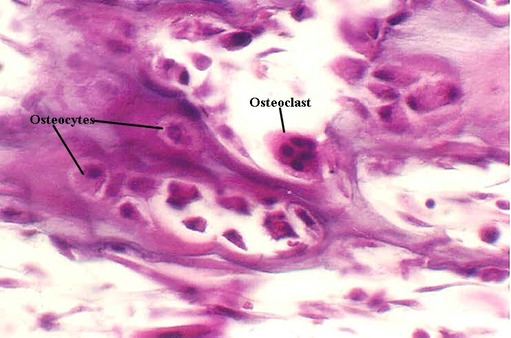
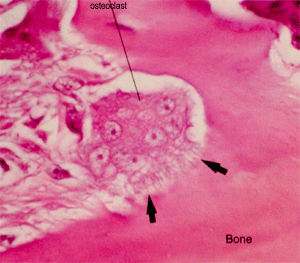
Mature bone forming cells embedded in lacunae within the bone matrix osteoblasts and osteocytes secrete organic matrix of bone osteoid converted into osteocytes when become embedded in matrix which calcifies soon after deposition.

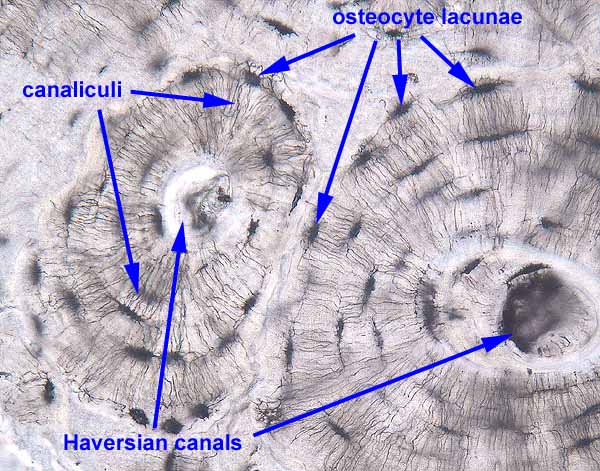
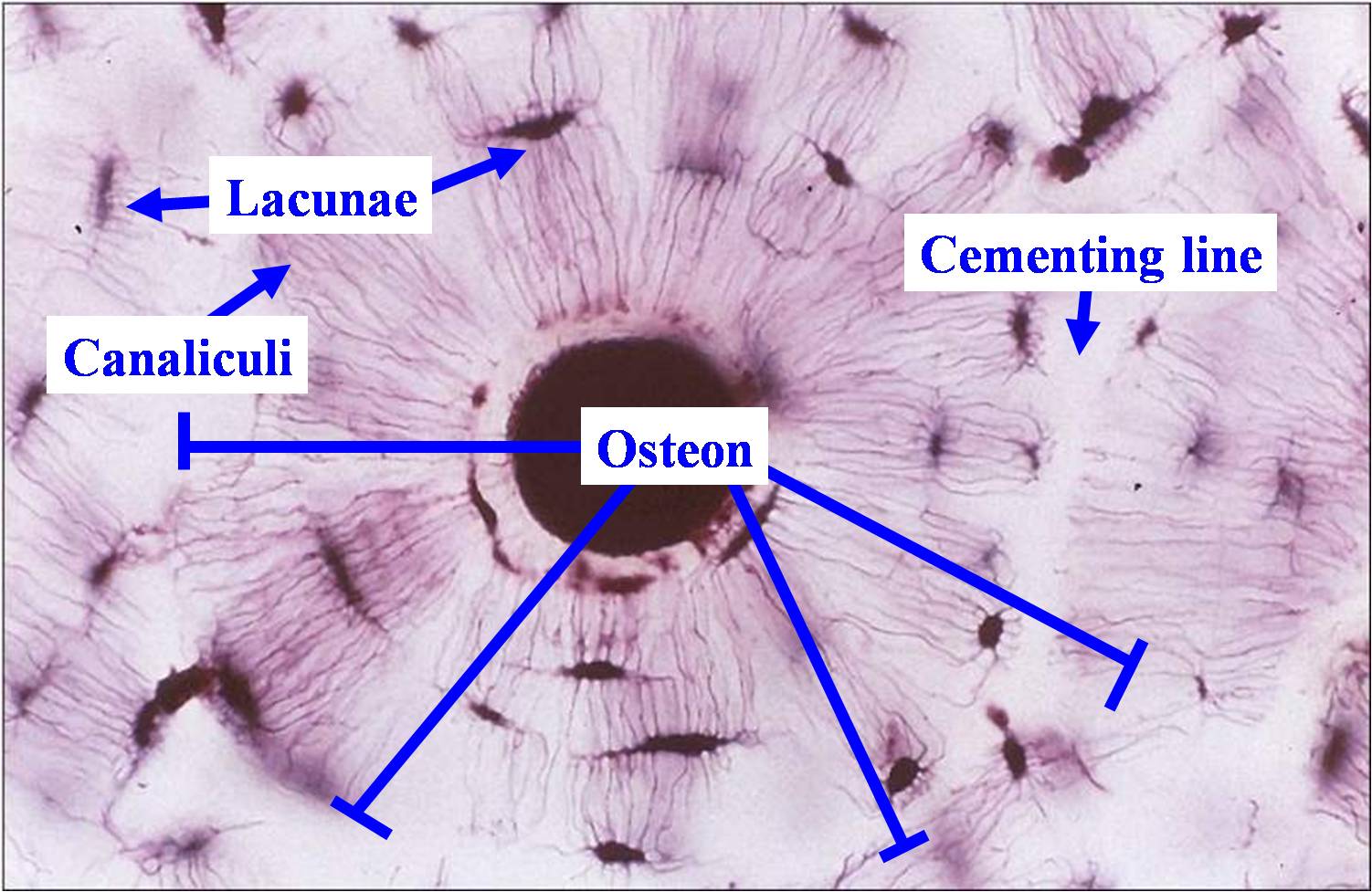
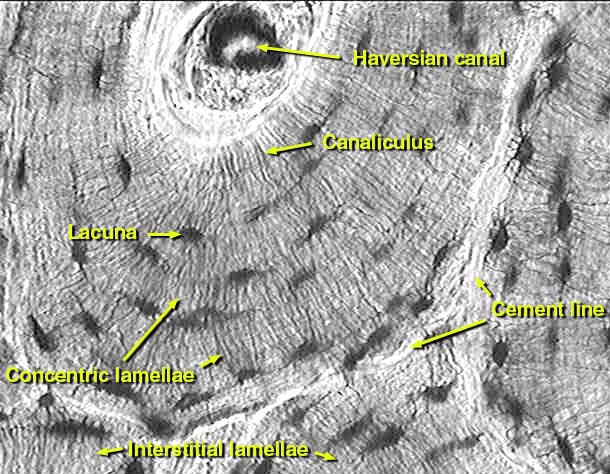
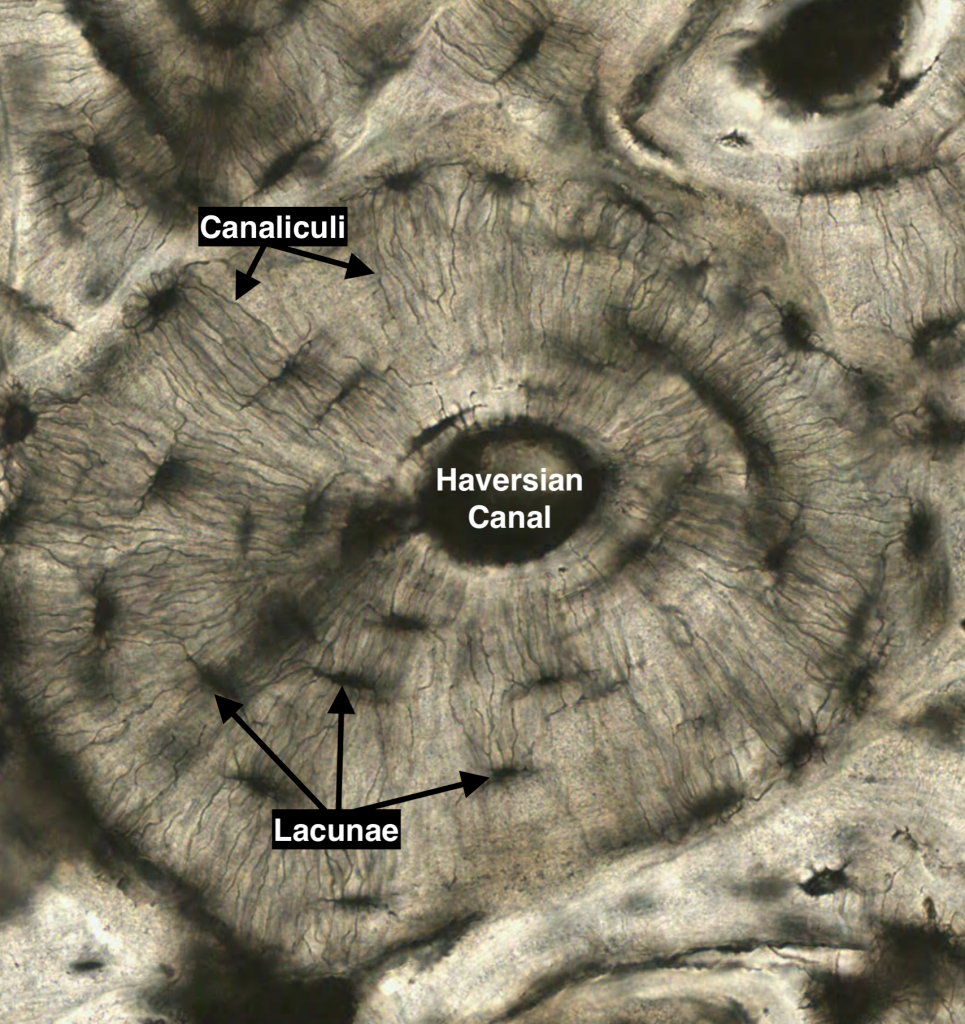
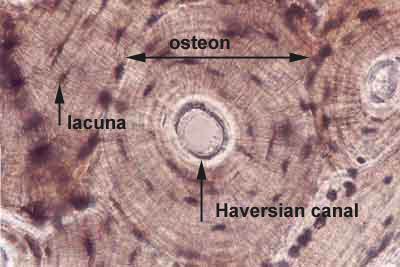
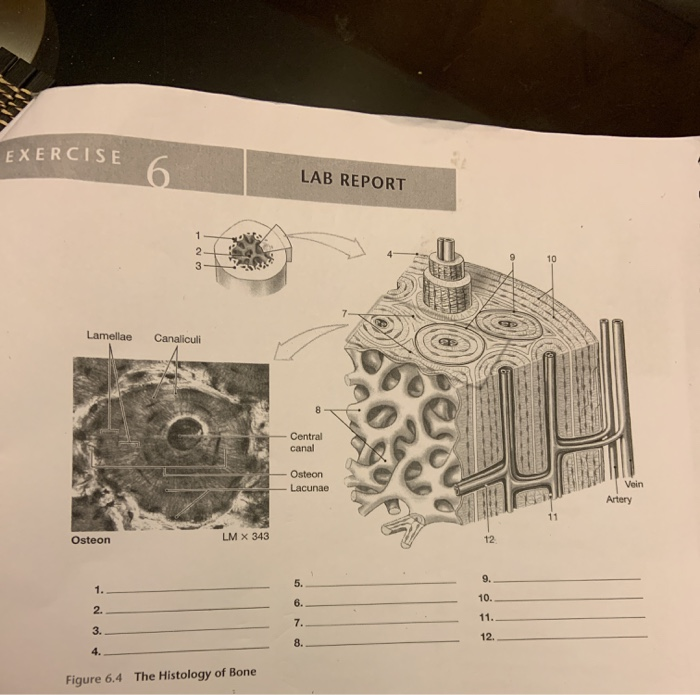
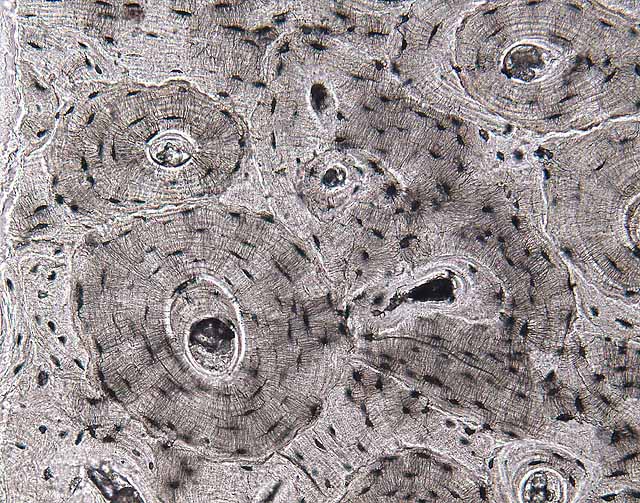
Lacunae histology. The lamellae of the haversian systems are created by osteoblasts. Lacunae refers to the small cavity in the substance of the bone containing an osteocyte. The matrix enclosed compartments that they sit in are called lacunae. Digital cytology cuts diagnosis time from days to minutes and improves quality of care.
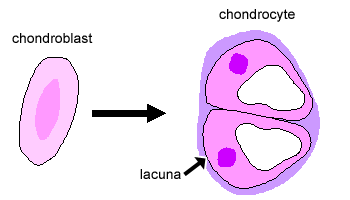
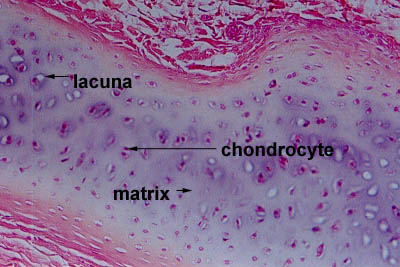
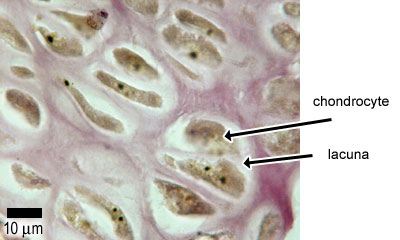
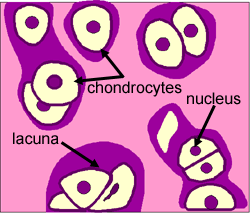
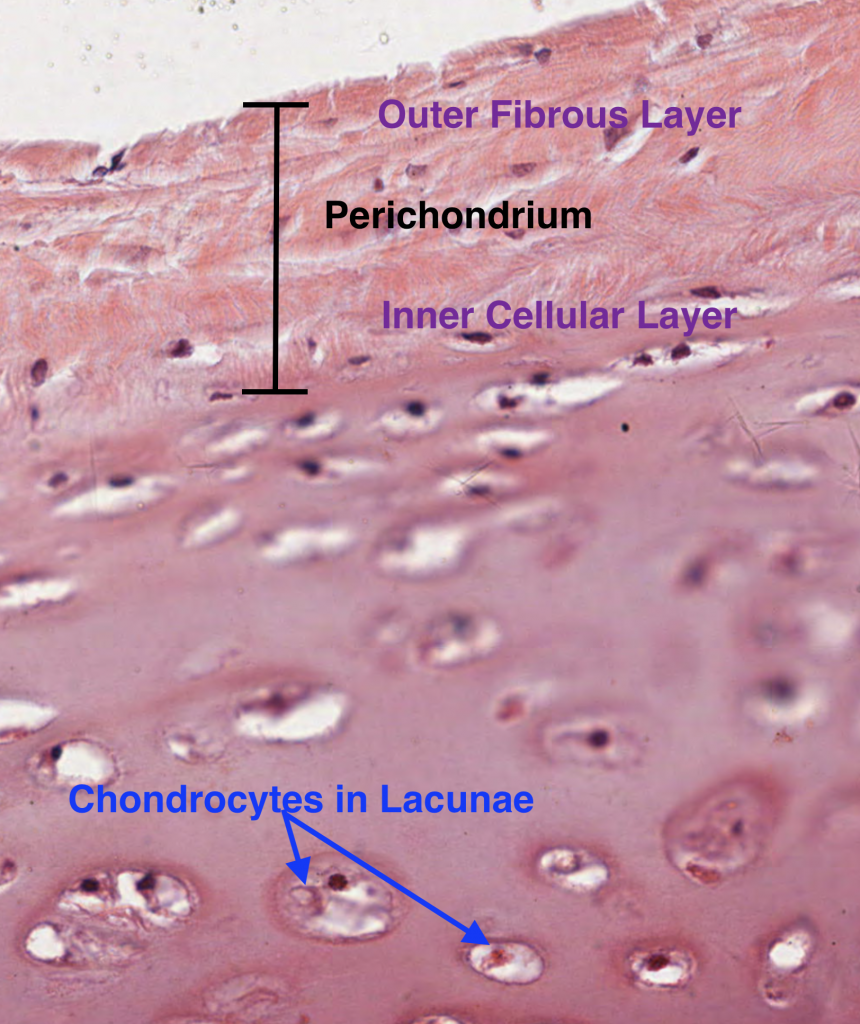
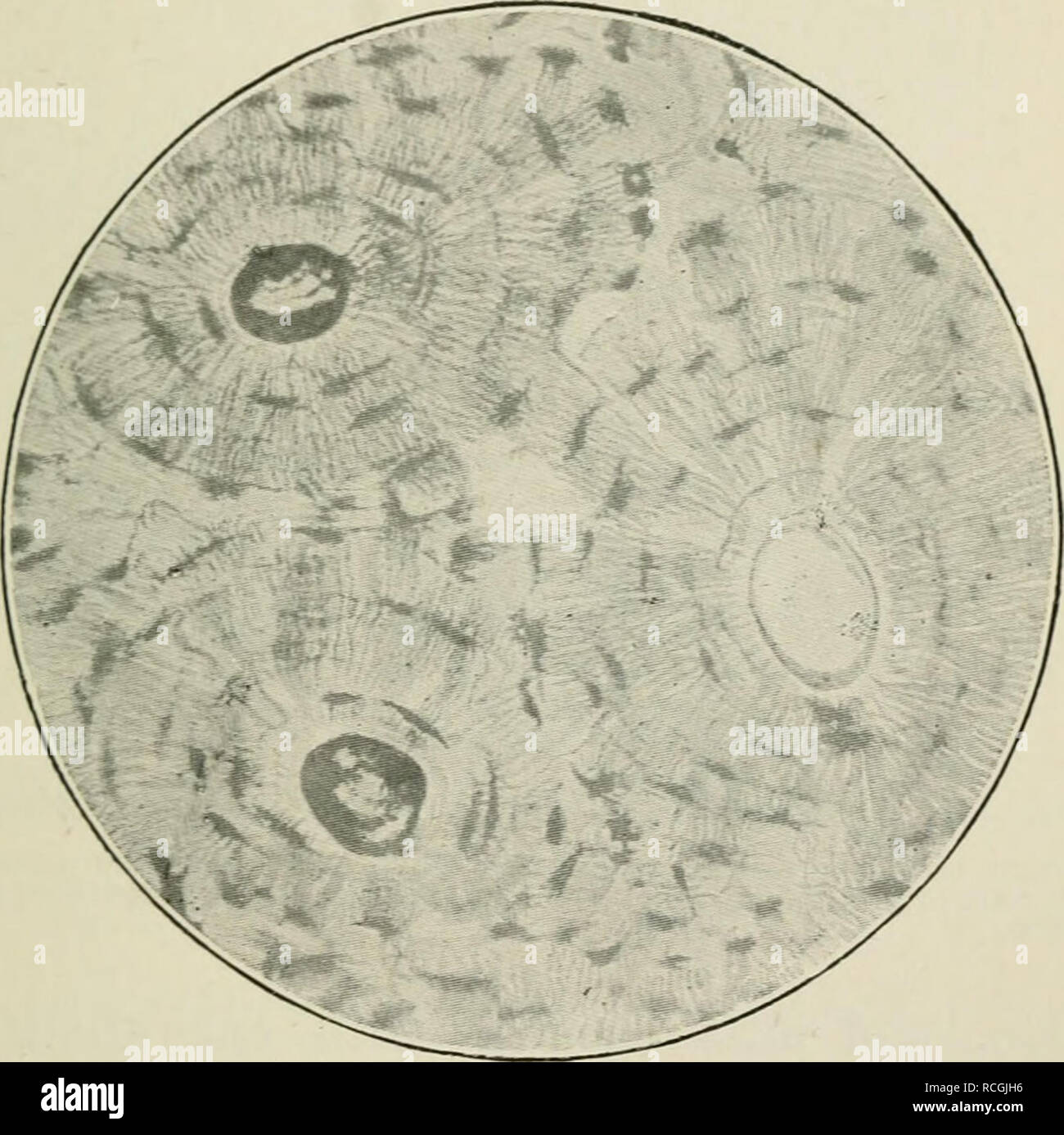
Lacunae little lakessmall pits. The latter is called cartilage lacuna. It may also be used to refer to the small cavity containing a chondrocyte in a cartilage tissue. These are channels for the transport for nutrients and waste.
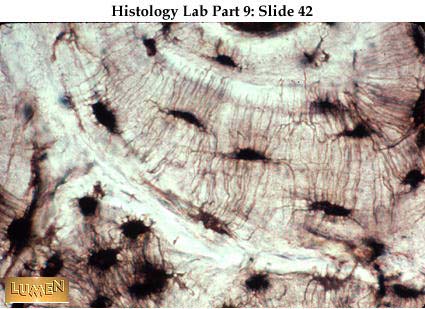
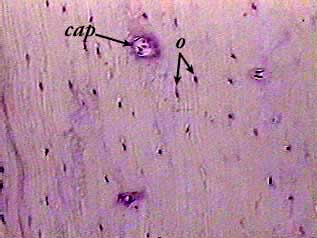
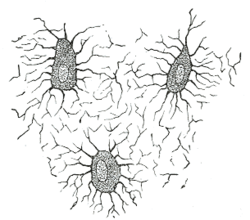
Osteocytes communicate with the haversian canal through cytoplasmic extensions that run through canaliculi small interconnecting canals. This diagram shows how an osteocyte sits in the calcified matrix. Osteocyte is an entrapped osteoblast in the matrix. Chondrocytes are important in synthesizing and maintaining components of the ecm.
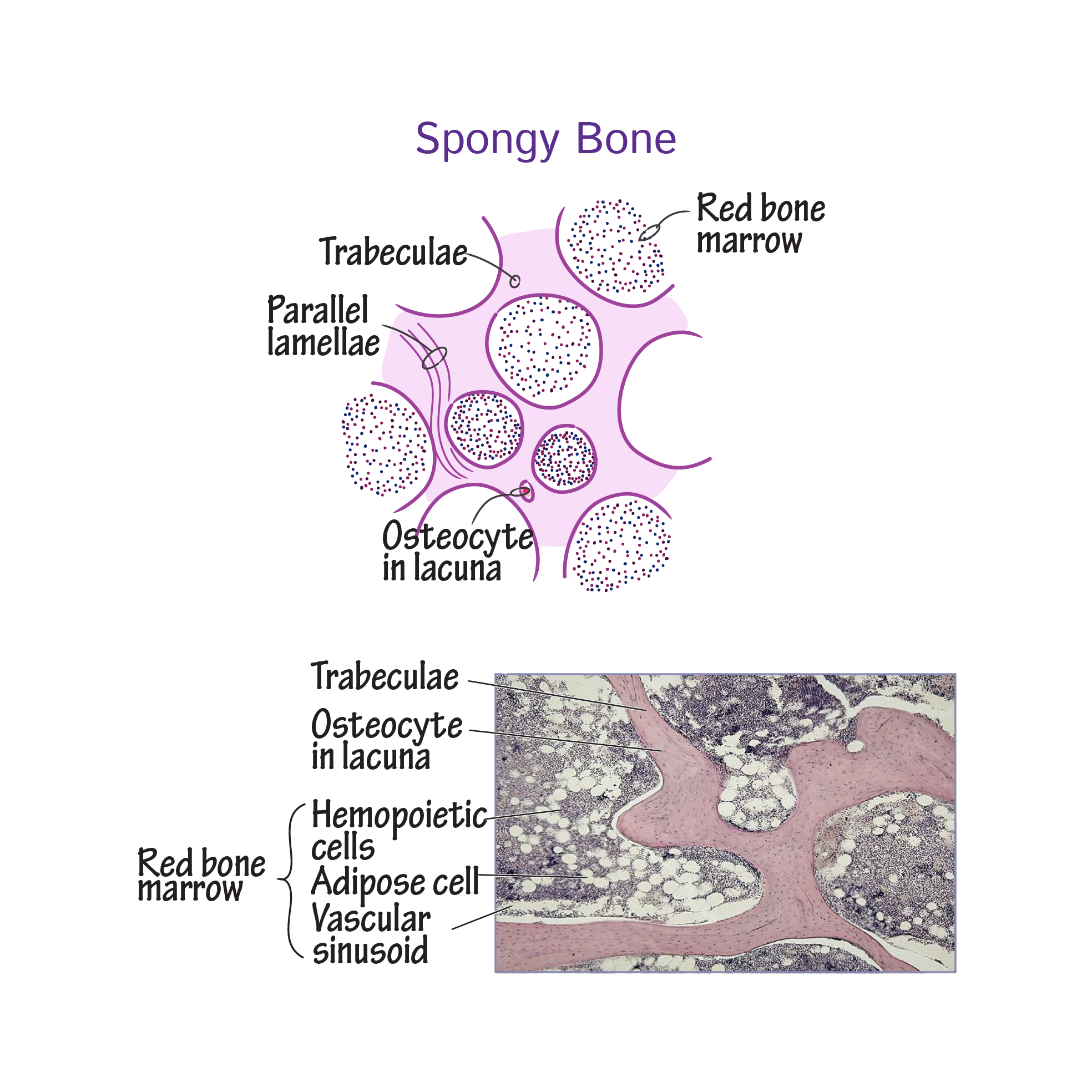
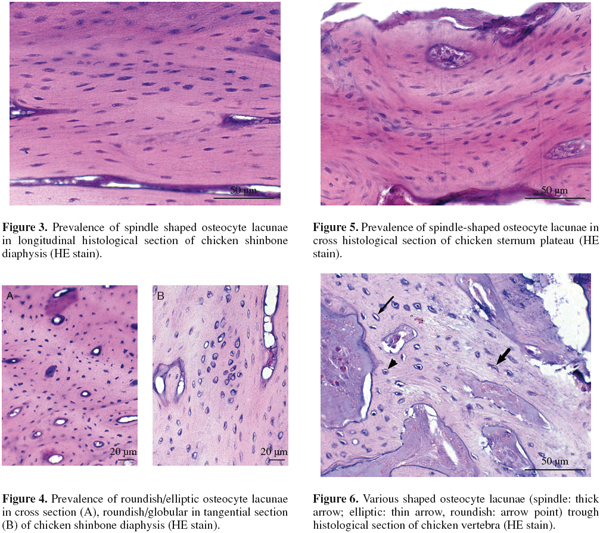
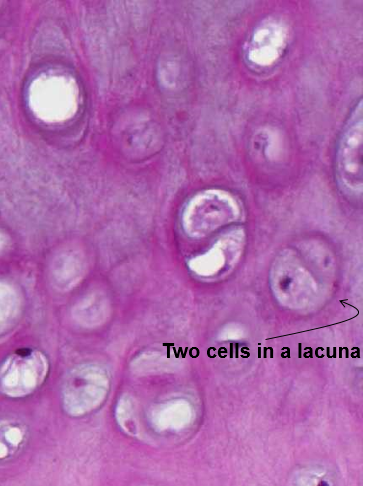
Learn how lacuna digital cytology can take your practice to the next level. Chondrocytes occupy relatively little of the hyaline cartilage mass. As these cells secrete matrix they become trapped in spaces called lacunae and become known as osteocytes. Bone lacuna a small cavity within the bone matrix containing an osteocyte and from which slender canaliculi radiate and penetrate the adjacent lamellae to anastomose with the canaliculi of neighboring lacunae thus forming a system of cavities interconnected by minute canals.
In histology a lacuna is a small space containing an osteocyte in bone or chondrocyte in cartilage. Osteocytes sit in the calcified matrix in small spaces called lacunae lacuna singular. Older chondrocytes contain fat droplets. In histology or anatomy lacuna plural.



















:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/1845/u2VPm5Ai4m0orGhZezDaQ_histology-hyaline-cartilage_english.jpg)












:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/3979/Qzj0RexMMaQQxDW5gL1xQ_Lacunae.png)



























:watermark(/images/watermark_5000_10percent.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/atlas_overview_image/1893/LMWu67nPEjziY7G5yghKdw_histology-bone-tissue-formation_english.jpg)